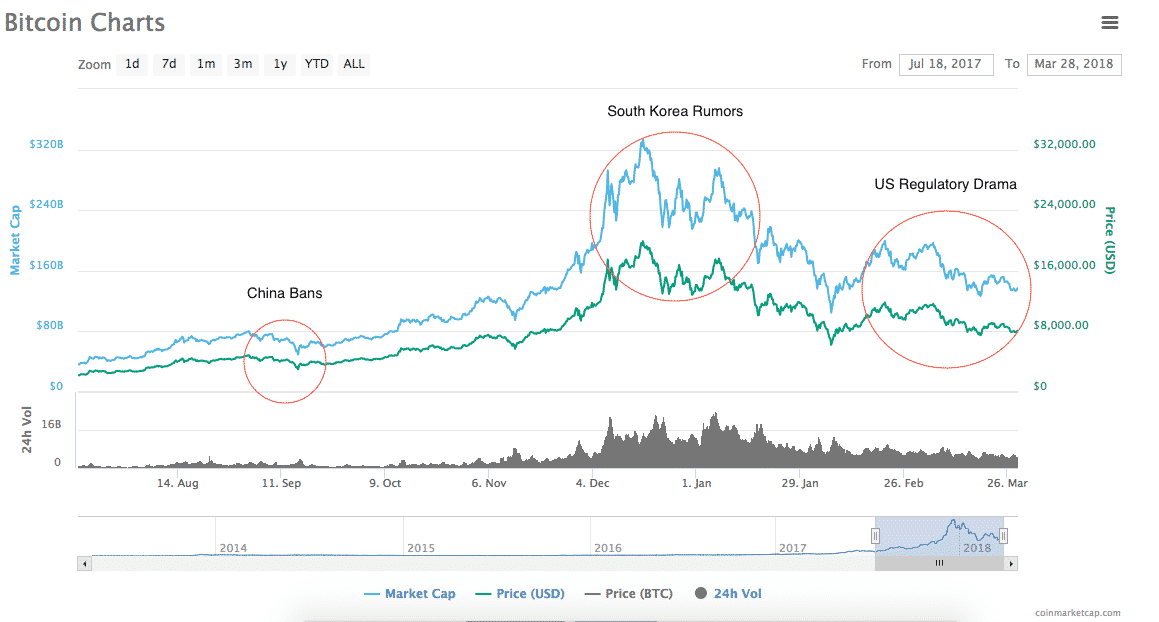
What causes bitcoin price fluctuation clause
To calculate the feerate for a transaction group, sum the fees paid by all the the group's unconfirmed transactions and divide that by the sum of the sizes for all those same transactions in weight units or vbytes. This means that miners attempting to maximize fee income can get good results by simply sorting what causes bitcoin price fluctuation clause feerate and including as many transactions as possible in a block:. For example, in the illustration below we see the average time between blocks based on the time they were received by a node during a one day period left axis and the corresponding effective maximum block size implied by that block production rate right axis, in million vbytes:. Debates on the legitimacy of digital currency never end, with speculation around possibilities of what causes bitcoin price fluctuation clause replacement of fiat money, an ensuing prospective governance mechanism and its function akin to that of central banks.

This complicates the task of maximizing fee revenue for miners. This makes the height of each transaction equal to the fee divided by the size, which is called the feerate: One of the primary mandates of central bank is to rein in inflation, while facilitating currency circulation and investment expansion.
Because only complete transactions can be added to a block, sometimes as in the example above the inability to include the incomplete transaction near the end of the block frees up space for one or more smaller and lower-feerate transactions, so when a block gets near full, a profit-maximizing miner will often ignore all remaining transactions that are too large to fit and include what causes bitcoin price fluctuation clause smaller transactions that do fit still in highest-feerate order:. Are financial meltdowns inevitable? The following sections describe the behavior of the reference implementation as of version 0. In this case, we can't, so no changes are made.

This means that miners attempting to maximize fee income can get good results by simply sorting by feerate and including as many transactions as possible in a block:. Wage increase is hard to keep up with CPI when assets are inflationary, what causes bitcoin price fluctuation clause thus put workers in a stringent vicious cycle. These transaction groups are then sorted in feerate order as described in the previous feerate section:. However, the rule that all outputs must be 0.

This section describes how the reference implementation selects which transactions to put into new blocks, with default settings. So how does a miner select which transactions to include? Every Bitcoin transaction spends zero or more bitcoins to zero or more recipients. Incidents like hacker attack, coding mistakes, fall down of major traders, changes in regulation and transaction size will affect the value of Bitcoin. Debates on the legitimacy of digital currency never end, with speculation around possibilities of its replacement of fiat money, an ensuing prospective governance mechanism and its function akin to that of central banks.
