Rules about posting transactions into taccounts in the ledger
Accounting is the mechanism used to record activities and transactions that occur within a business. In its simplest terms, Accounting is the "language of rules about posting transactions into taccounts in the ledger. The first general rule of accounting is that every transaction is recorded. Rules about posting transactions into taccounts in the ledger has been said that businesses that do not record transactions, or incorrectly record transactions, are committing fraud, although this is not necessarily the case.
Fraud is part of a much broader area called material misstatement which also can include error. An error is not necessarily fraud under the law. While there are exceptions to this rule, the guidance for applying those exceptions is specifically defined by G. P, and is applicable to all businesses. The second general rule of accounting is that transactions are recorded using what is called a "double-entry" accounting method.
Originally developed in Italy in the s, double-entry means that for a complete record of a transaction, two entries are made. In this example, one transaction contained two entries. This takes a little time to get used to, but it is a critical concept in basic accounting.
Double entry is tied to the concept of Debits and Credits, which you will learn about in the next section. The act of recording transactions is commonly referred to as making journal entries. In a few more paragraphs, we'll discuss what a journal entry looks like.
The third general rule of accounting is that every recorded transaction is captured in a log called the "General Journal. In general, "Accounting is the art of recording, classifying, summarizing and interpreting rules about posting transactions into taccounts in the ledger business transaction. To make this easier, we can follow the golden rules of accounting.
Accounts are one of three basic types:. The Sales account is opened for recording the sales of goods or services. At the end of the financial period, the total sales are transferred to the revenue statement account Profit and Loss Account or Income and Expenditure Account. Similarly, expenses during the financial period are recorded using the respective Expense accounts, which are also transferred to the revenue statement account.
The net positive or negative balance profit or loss of the revenue statement account is transferred to reserves or capital account as the case may be. An ' account' is a specific location for recording transactions of a like kind. For example, in the gas-for-cash transaction above, two accounts are used, a "Cash" account and a "Gas" account.
Unused by that example, but described is an account for "Equipment" which would include the portable gas can and the lawn mower. When a transaction occurs, a document is produced. Most of the time, these documents are external to the business, however, they can also be internal documents, such as inter-office sales. These documents are referred to as a source document. Some examples of source documents are:. These source documents are then recorded in a Journal. This is also known as a book of first entry.
The journal records both sides of the transaction recorded by the source document. These write-ups are known as Journal entries. These Journal entries are then transferred to a Ledger. The group of accounts is called ledger. A ledger is also known as a book of accounts. The purpose of a Ledger is to bring together all of the transactions for similar activity.
For example, if a company has one bank account, then all transactions that include cash would then be maintained in the Cash Ledger. This process of transferring the values is known as posting. Once the entries have all been posted, the Ledger accounts are added up in a process called Balancing. This will make much more sense when you learn about Debits and Credits. Balancing implies that the sum of all Debits equals the sum of all Credits.
A particular working document called an unadjusted trial balance is created. This lists all the balances from all the accounts in the Ledger. Notice that the values are not posted to the trial balance, they are merely copied. At this point accounting happens.
The accountant produces a number of adjustments which make sure that the values comply with accounting principles. These values are then passed through the accounting system resulting in an adjusted trial balance.
This process continues until the accountant is satisfied. Financial statements are drawn from the trial balance which may include:. For the purposes of accounting, please forget what you know about credits and debits.
In accounting, debit Dr. An account will have either a " normal credit balance " or a " normal debit balance ", depending on the type of account. The normal balance indicates which side of the account the amount goes to when the account balance increases.
For example, the account 'Cash' has a normal debit balance: Debits and credits may be derived from the rules about posting transactions into taccounts in the ledger accounting equation. They result from the nature of double entry bookkeeping.
Two entries are made in each balanced transaction, a debit and a credit. This allows the accounts to be balanced to check for entry or transaction recording errors. In accounting this is generally rewritten from the perspective of the business or commercial entity the books detail:.
Entries in the books rules about posting transactions into taccounts in the ledger in pairs and track the advantage or asset of the company simultaneously with the disadvantage or liability. In this view the Owner's equity is a claim of the investor against the company.
Even when a business has a single owner we make a distinction between the owner's assets and the assets of the business. For example if the owner gives a van to the business this will count as capital introduced, if the owner takes a salary this will be accounted for as drawings.
All accounting transactions are first recorded in a journal. The most common of these is the General Journalsometimes also known as the Book of Original Entry, because it is the first place a transaction is entered into the books.
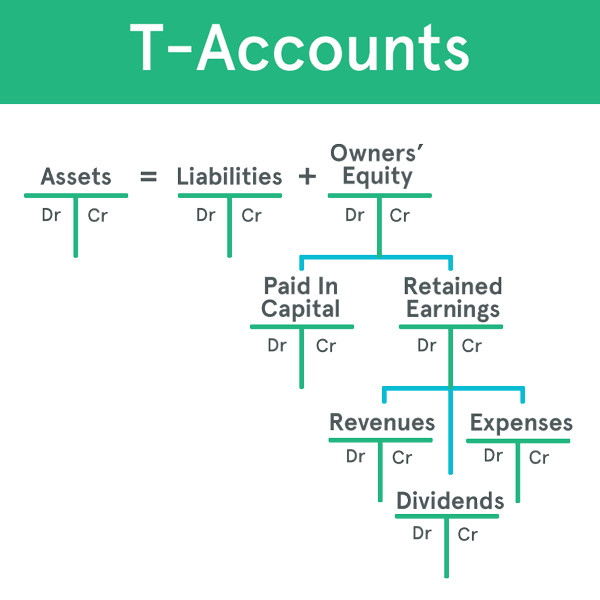
Journal Entries are made from source documentswhich can be anything from receipts to invoices to bank statements. These two entries show the premise of double-entry accounting. Note that the form of what is written is as important as the actual text:. One representation of an account is called the T-accountshown above.
A T-account contains just the basic elements of the account, so it lacks the necessary detail for use in bookkeeping operations. However, it has its uses as both an illustrative tool rules about posting transactions into taccounts in the ledger a quick reference. Each account needs to have a unique Account Namesuch as Cash, for ease of reference later on.
In modern accounting systems, you will often see an account number alongside the name in order to facilitate report generation and computer entry.
Under the bar are the debit from the Latin debereto owe and credit credereto believe columns. As it shows in the example above, the balance of a T-account can be figured by first totaling each column. Second, subtract the smaller subtotal from the larger, and finally placing the total in the larger number's column. While a T-Account is useful for quickly summarising an account's balance, it only contains a fraction of the information that was recorded in the Journal. A central axiom for accounting is the accounting equation above.
Depending on the type of company involved, Owner's Equity may be "Shareholder's" or simply "Equity", but the equation holds. The list of all of the accounts along with their respective account numbers is called the Chart of Accounts. Asset accounts indicate what a company owns. This can be actual possession or the right to take possession, such as a loan extended to another company. Some assets are identifiable by the term "Receivable".
Assets have rules about posting transactions into taccounts in the ledger normal debit balance. Liability accounts indicate what a company owes to others. Examples of liabilities include loans to be repayed and services that have been paid for that the company hasn't performed yet. Many liabilities can be identified by the term "Payable" in their account name.
Liabilities have a normal credit balance. Equity accounts are a group of accounts that represent the amount of owner's equity in the business.
There are four main types of Equity accounts:. Assets and liabilities should be recorded at the price at which they were acquired. This is to ensure a reliable price; market values can fluctuate and be different between differing opinions, so the price of acquisition is used.
Expenses should be matched with revenues. The expense is recorded in the time period it is incurred, which means the time period that the expense is used to generate revenue. This means that you can pay for an expense months before it is actually recorded, as the expense is matched to the period the revenue is made. Revenues should not be recorded until the earnings process is almost complete and there is little uncertainty as to whether or not collection of payment will occur.
This means that revenue is recorded when it is earned, which means the job is complete.