Calculating recombination frequency map units
The units of genetic distance are called map units mu or centiMorgans cMin honor of Thomas Hunt Morgan. The units of genetic distance are called map units mu or centiMorgans cMin honor of Thomas Hunt Morgan. The question is more one of frequency.

The method for calculating recombination frequency map units of these long chromosomes is shown below. If necessary, draw out all the possible genotypes and corresponding phenotypes to convince yourself that these numbers are correct. Observing these kinds of segregation patterns indicates that the mutation and the markers are on different chromosomes. These numbers are identical to those previously calculated for picking Unc progeny and looking for Ste Unc in the next generation. CuboCube software is open-source.

In general, basing linkage designation on a small number of data points fewer than 20 should be avoided. Regulation of Gene Expression Chapter A genetic map shows the map distance, in cM, that separates any two loci, and the position of these loci relative to all other mapped loci. Interestingly, by the time we get to
In addition, this strain can be used for three-point mapping. For example, in Arabidopsis1. Book Contributors of Open Genetics. These numbers are identical to those previously calculated for picking Unc progeny and looking for Ste Unc in the next generation. Similar calculations can be carried out for various genetic distances.

For a discussion of additional two-point mapping strategies as well as potentially useful formulas for correlating map distances with phenotypes, see Hodgkin In addition, this strain can calculating recombination frequency map units used for three-point mapping. The source code is available at our public Github repository. Often we calculating recombination frequency map units carry out traditional two-point mapping using strains that contain two adjacent chromosomal markers, as the strains generated by these crosses can potentially be used later for three-point genetic mapping. For example, if you happened to observe three plates out of 25 with M A B animals and one plate with M A animals, that would suggest that m lies to right of b and is at some distance from the markers.
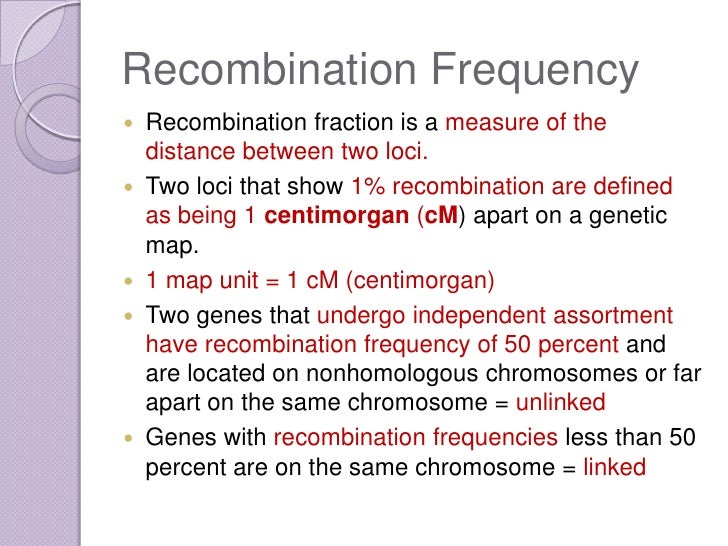
This usually is not an issue because we tend to carry out two-point mapping with markers at the chromosome center, guaranteeing distances no greater than about This latter number should sound familiar; it's the same percentage you would get if the ste and unc mutations were on separate chromosomes. Seeing segregation patterns of this type tells us that m and a b reside on the same chromosome and also that m resides close to or in between the markers calculating recombination frequency map units and b.
There are often multiple ways to carry out two-point mapping using the same set of markers. In calculating recombination frequency map units, basing linkage designation on a small number of data points fewer than 20 should be avoided. The genetic patterns described above are for the ideal situation where there is no ambiguity in the determination of chromosomal location. In thinking about this, keep in mind that these "rare" recombinant chromosomes will usually - by chance - wind up paired with one of the non-recombinant parental chromosomes in a fertilized zygote. But what happens when the mutation lies to one side of the markers, perhaps at some distance?

The correlation between recombination frequency and actual chromosomal distance is more accurate for short distances low RF values than long distances. Similar calculations can be carried out for various genetic distances. In the calculating recombination frequency map units that the M phenotype is lethal, this may be a useful strain for maintaining m as a balanced heterozygote. In addition, a wild-type animal can now fail to throw both M and AB animals.

For example, if the marker and mutation are 1. The genetic patterns described above are for the ideal situation where there is no ambiguity in the determination of chromosomal location. As the distance between the mutation and marker increases, this frequency decreases.