64 bit ripple carry adders
The gate delay can easily be calculated by inspection of the full adder circuit. After P and G are generated, the carries for every bit position are created. The circuit produces a two-bit output.
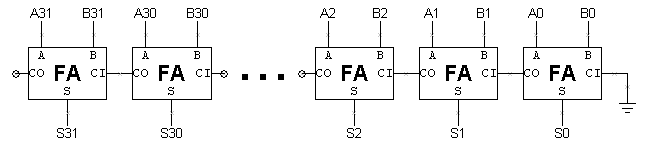
This kind of adder is called a ripple-carry adder RCAsince each carry bit "ripples" to the next full adder. Using only two types of gates is convenient if the circuit is being implemented using simple IC chips which contain only one gate type per 64 bit ripple carry adders. The truth table for the half adder is:. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. It is possible to vary the length of these blocks based on the propagation delay of the circuits to optimize computation time.

It is possible to create a logical circuit using multiple full adders 64 bit ripple carry adders add N -bit numbers. Views Read Edit View history. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Computer arithmetic Adders electronics Binary logic. The half adder adds two single binary digits A and B.

It is possible to vary the length of these blocks based on the propagation delay of the circuits to optimize computation time. This can be used at multiple levels to make even larger adders. This kind of circuit is most notably used in multipliers, which is why these circuits are also known as 64 bit ripple carry adders and Wallace multipliers. The sum and the carry may be fed into two inputs of the subsequent 3-number adder without having to wait for propagation of a carry signal.
In other projects Wikimedia Commons. The half adder adds two single binary digits A and B. An adder is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. Assumed that an XOR-gate takes 1 delays to 64 bit ripple carry adders, the delay imposed by the critical path of a full adder is equal to.

In many computers and other kinds of processors adders are used in the 64 bit ripple carry adders logic units or ALU. To reduce the computation time, engineers devised faster ways to add two binary numbers by using carry-lookahead adders CLA. Some other multi-bit adder architectures break the adder into blocks. It is possible to create a logical circuit using multiple full adders to add N -bit numbers. The input variables of a half adder are called the augend and addend bits.

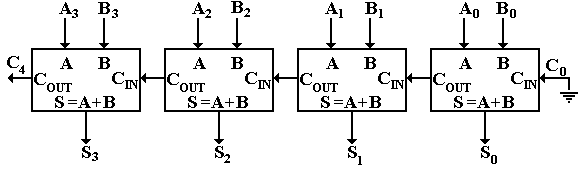
Other signed number representations require more logic around the basic adder. It is possible to create a logical circuit using multiple full adders to add N -bit numbers. Retrieved from " https: A one-bit full-adder adds three one-bit numbers, often written as ABand C in ; A and B are the operands, and C in 64 bit ripple carry adders a bit carried in from the previous less-significant stage. Using only two types of gates is convenient if the circuit is being implemented using simple IC chips which contain only one gate type per chip.

Although adders can be constructed for many number representationssuch as binary-coded decimal or excess-3the most common adders operate on 64 bit ripple carry adders numbers. In other projects Wikimedia Commons. In many computers and other kinds of processors adders are used in the arithmetic logic units or ALU. If the addends are exactly three, the layout is known as the carry-save adder.

The gate delay can easily be calculated by inspection of the full adder circuit. A full adder can be implemented in many different ways such as with a 64 bit ripple carry adders transistor -level circuit or composed of other gates. If the addends are exactly three, the layout is known as the carry-save adder. Written at Heverlee, Belgium.