Zero knowledge proof blockchain unconfirmed
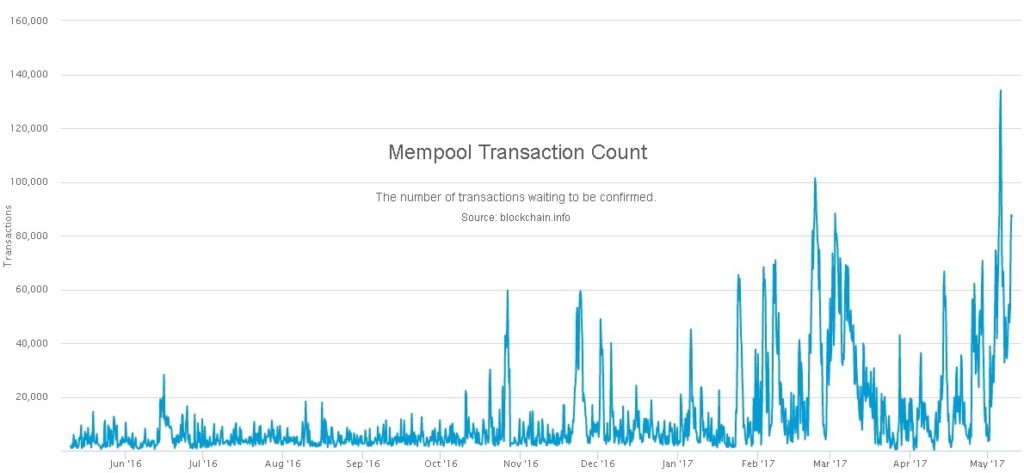
Hash starting with certain number of zero knowledge proof blockchain unconfirmed. Node 1 adds the transaction to its transaction pool or list of pending transactions. This is called reaching consensus. Each transaction is digitally signed and involves one or more participants accompanied by a record of what happened e. Blockchain Platforms This section is a short overview of different blockchain platforms currently in use.
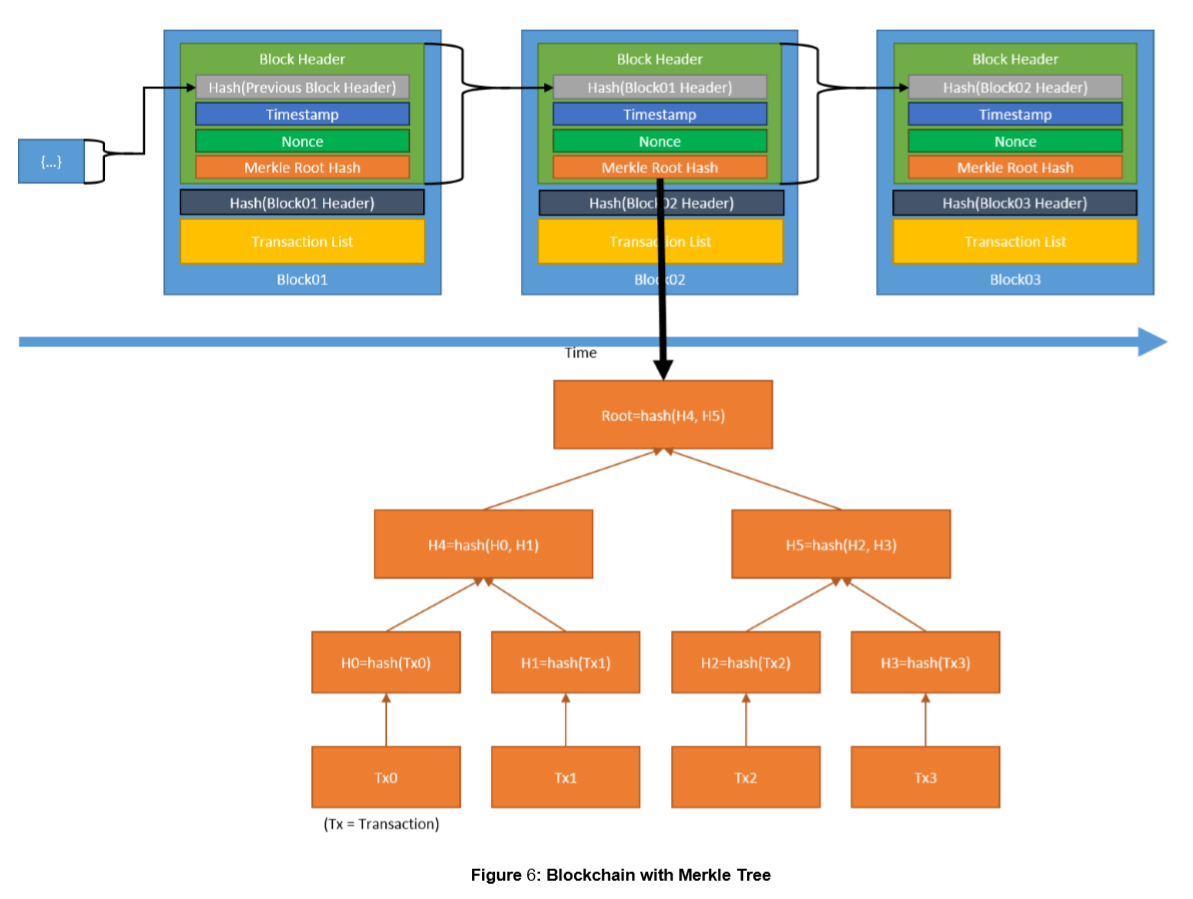
Everyone can read all transactions. Total amount of assets transferred. Modifying any block will invalidated all block hashes after it in the blockchain and will be detected.
Using a blockchain as a storage medium will be slow and consume many resources. Each node removes any transactions zero knowledge proof blockchain unconfirmed are in the newly mined block from its list and starts mining a new block. Mining a block is a difficult task but verifying that a mined block is valid is easy. Each transaction usually has at least these components:
Receiving nodes check the validity of the block as mentioned beforeadd it to their block chain and pass zero knowledge proof blockchain unconfirmed to other nodes. Can write access be revoked? Modifying any block will invalidated all block hashes after it in the blockchain and will be detected. Created when original Bitcoin blockchain had a hard fork in July after introduction of Segwit. Each transaction is passed around the network.
Created when original Zero knowledge proof blockchain unconfirmed blockchain had a hard fork in July after introduction of Segwit. Does not store the complete blockchain or create new blocks and passes data to other nodes. Once malicious users control a decent number of nodes, they can: First block of blockchain and often the only pre-configured block.

Nodes need to perform a difficult task mining a block to be granted permission to create a zero knowledge proof blockchain unconfirmed block and be rewarded in this case bitcoins. Difficulty is adjusted to have a new block every 10 minutes. Impact of quantum computing on common cryptographic algorithms taken directly from draft. How do participants decide what transactions are valid? The other way is possible, smaller assets can be combined to make a larger assets.
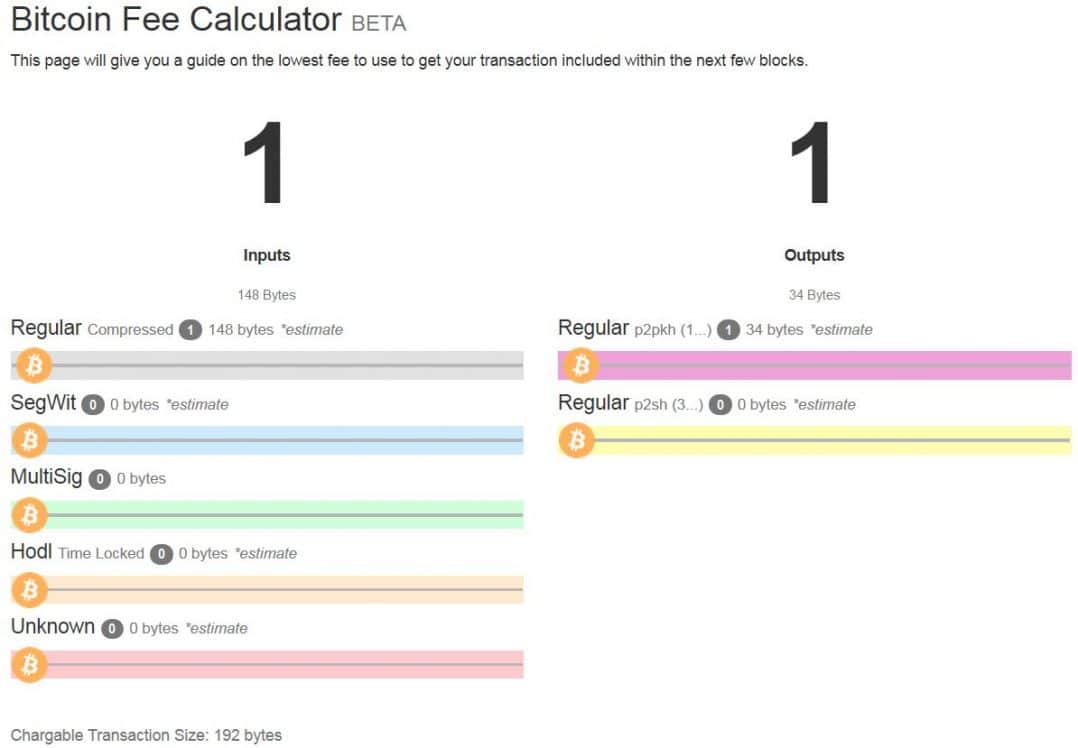
Nodes agree on a consensus method how new blocks are added to the chain. Pass data to full nodes to be processed. Transaction fees are optional but needed as time goes on:
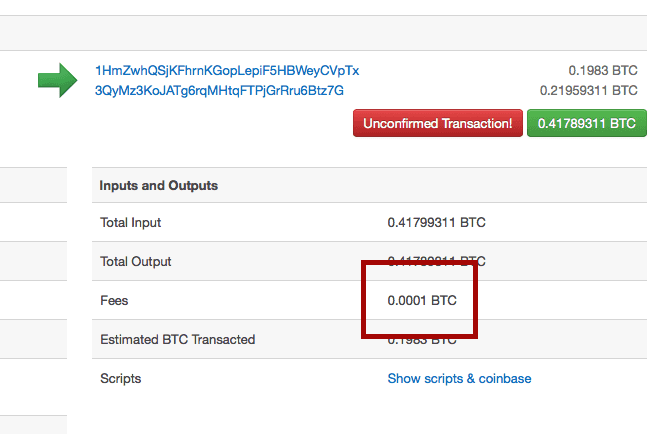
Bitcoin transactions only a small subset of it. Blockchains often use monetary rewards cryptocurrency for mining new blocks to motivate users to act fairly. What should be stored?