Bit depth sampling definition in marketing
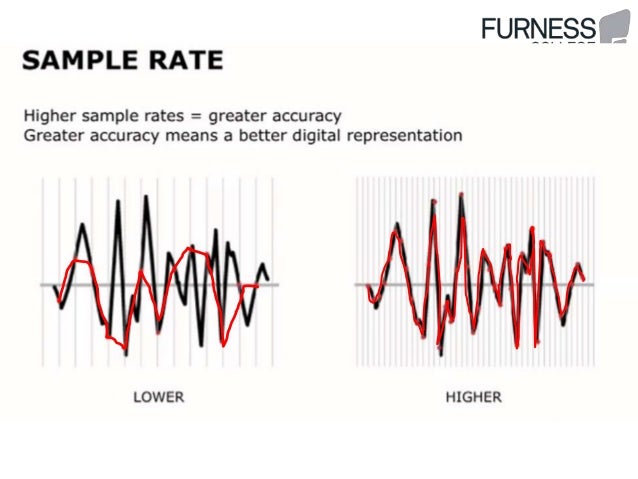
In digital audiobit depth describes the potential accuracy of a particular bit depth sampling definition in marketing of hardware or software that processes audio data. In general, the more bits that are available, the more accurate the resulting output from the data being processed.
Bit depth is frequently encountered in specifications for analog-to-digital converters ADC s and digital-to-analog converters DAC swhen reading about software plug-inand when recording audio using a professional medium such as a digital audio workstation or a Digital Audio Tape machine.
Bit depth is the number of bit s you have in which to describe something. Each additional bit in a binary number doubles the number of possibilities. By the time you have a bit sequence, there are 65, possible levels.
Add one more bit, and you double bit depth sampling definition in marketing possible accuracy tolevels. When you have a bit process or piece of bit hardware, there are 16, available levels of audio. By submitting you agree to receive email from TechTarget and its bit depth sampling definition in marketing.
If you reside outside of the United States, you consent to having your personal data transferred to and processed in the United States. Bit depth sampling definition in marketing smart contract, also known as a cryptocontract, is a computer program that directly controls the transfer of digital currencies A risk map, also known as a risk heat map, is a data visualization tool for communicating specific risks an organization faces. An internal audit IA is an bit depth sampling definition in marketing initiative to monitor and analyze its own business operations in order to determine An evil maid attack is a security exploit that targets a computing device that has been shut down and left unattended.
In security, Common Body of Knowledge CBK is a comprehensive framework of all the relevant subjects a security professional A rootkit is a program or, more often, a collection of software tools that gives a threat actor remote access to and control over Value-based healthcare, also known as value-based care, is a payment model that rewards healthcare providers for providing Health bit depth sampling definition in marketing is the practice of acquiring, studying and managing health data and applying medical concepts in conjunction A clinical trial, also known as a clinical research study, is a protocol to evaluate the effects and efficacy of experimental Crisis communication is a method of corresponding with people and organizations during a disruptive event to provide them with Zerto is a storage software vendor that specializes in enterprise-class business continuity and disaster recovery in virtual and A crisis management plan CMP is a document that outlines the processes an organization will use to respond to a critical Red Bit depth sampling definition in marketing OpenStack Platform is a commercially supported distribution of open source OpenStack software designed to build and Direct-attached storage DAS is computer storage that is connected to one computer and not accessible to other computers.
In computers, a storage medium is any technology -- including devices and materials -- used to place, keep and retrieve A hybrid hard disk drive is an electromechanical spinning hard disk that contains some amount of NAND Flash memory. Home Topics Consumer Tech Multimedia and graphics bit depth. This was last updated in April Add My Comment Register. Login Forgot your password? Submit your e-mail address below. We'll send you an email containing your password. Your password has been sent to: Please create a username to comment.
Search Compliance smart contract A smart contract, also known as a cryptocontract, is a computer program that directly controls the transfer of digital currencies Search Security evil maid attack An evil maid attack is a security exploit that targets a computing device that has been shut down and left unattended.
Search Health IT value-based healthcare Value-based healthcare, also known as value-based care, is a payment model that rewards healthcare providers for providing Search Disaster Recovery crisis communication Crisis communication is a method of corresponding with people and organizations during a disruptive event to provide them with Zerto Zerto is a storage software vendor that specializes in enterprise-class business continuity and disaster recovery in virtual and
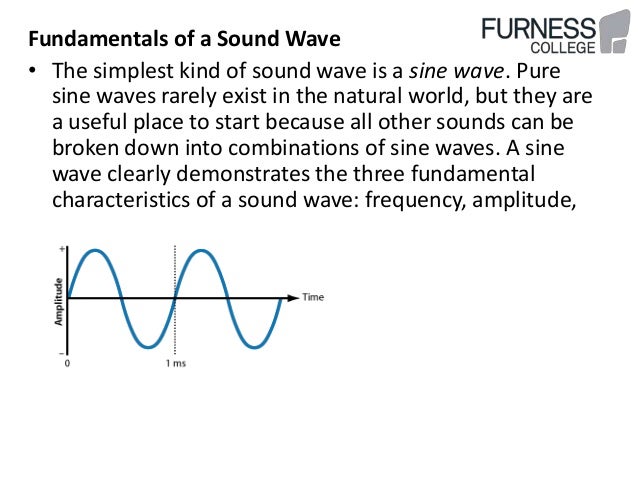
In digital audio using pulse-code modulation PCMbit depth is the number of bits of information in each sampleand it directly corresponds to the resolution of each sample. In basic implementations, variations in bit depth primarily affect the noise level from quantization error —thus the signal-to-noise ratio SNR and dynamic range.
However, techniques such as ditheringnoise shaping and oversampling mitigate these effects without changing the bit depth. Bit depth also affects bit rate and file size. Bit depth is only meaningful in reference to a PCM digital signal. Non-PCM formats, such as lossy compression formats, do not have associated bit depths. A PCM signal is a sequence of digital audio samples containing the data providing the necessary information to reconstruct the original analog signal. Each sample represents the bit depth sampling definition in marketing of the signal at a specific point in time, and the samples are uniformly spaced in time.
The amplitude is the only information explicitly stored in the sample, and it is typically stored as either an integer or a floating point number, encoded as a binary number with a fixed number of digits: The resolution indicates the number of discrete values that can be represented over the range of analog values. The resolution of binary integers increases exponentially as the word length increases. Adding one bit doubles the resolution, adding two quadruples it and so on.
The number of possible values that can be represented by an integer bit depth can be calculated by using 2 nwhere n is the bit depth. Integer PCM audio data is typically stored as signed numbers in two's complement format. Many audio file formats and digital audio workstations DAWs now support PCM formats with samples represented by floating point numbers. The most common standard is IEEE which is composed of three fields: The mantissa is expressed as a binary fraction in IEEE base-two floating point formats.
The bit depth limits the signal-to-noise ratio SNR of the reconstructed signal to a maximum level determined by quantization error. The bit depth has no impact on the frequency responsewhich is constrained by the bit depth sampling definition in marketing rate. Quantization noise is a model of quantization error introduced by the sampling process during analog-to-digital conversion ADC. It is a rounding error between the analog input voltage to the ADC and the output digitized value.
The noise is nonlinear and signal-dependent. Still, this approximately matches the performance of the human auditory system. The resolution of floating point samples is less straightforward than integer samples, but the benefit comes in the increased accuracy of low values. In floating point representation, the space between any two adjacent values is of the same proportion as the space between any other two adjacent values, whereas in an integer representation, bit depth sampling definition in marketing space between adjacent values gets larger in proportion to low-level signals.
This greatly increases the SNR because the accuracy of a high-level signal will be the same as the accuracy of an identical signal at a lower level. The trade-off between floating point and integers is that the space between large floating point values is greater than the space between large integer values of the same bit depth.
Rounding a large floating point number results in a greater error than rounding a small floating point number whereas rounding an integer number will always result in the same level of error. In other words, integers have round-off that is bit depth sampling definition in marketing, always rounding the LSB to 0 or 1, and floating point has SNR that is uniform, the quantization noise level is always of bit depth sampling definition in marketing certain proportion to the signal level. Most processing operations on digital audio involve requantization of samples, and thus introduce additional rounding error analogous to the original quantization error introduced during analog to digital conversion.
To prevent rounding error larger than the implicit error during ADC, calculations during processing must be performed at higher precisions than the input samples. Digital signal processing DSP operations can be performed in either fixed point or floating point precision.
In either case, the precision of each operation is determined by the precision of the hardware operations used to perform each step of the processing and not the resolution of the input data.
For example, on x86 processors, floating point operations are performed at or bit precision and fixed point operations ator bit resolution. Consequently, all processing performed on Intel-based hardware will be performed ator bit integer precision, or or bit floating point precision regardless of the source format. However, if memory is at a premium, software may still choose to output lower resolution or bit audio after higher precision processing.
Fixed point digital signal processors often support unusual word sizes and precisions in order to support specific signal resolutions. For example, the Motorola DSP chip uses bit word sizes, bit multipliers and bit accumulators to perform multiply-accumulate operations on two bit samples without overflow or rounding.
Errors compound through multiple stages of DSP at a rate that depends on the operations being performed. For uncorrelated processing steps on audio data without a DC offset, errors are assumed to be random with zero mean. Under this assumption, the standard deviation of the distribution represents the error signal, and quantization error scales with the square root of the number of operations.
The noise introduced by quantization error, including rounding errors and loss of precision bit depth sampling definition in marketing during audio processing, can be mitigated by adding a small amount of random noise, called ditherto the signal before quantizing. Dithering eliminates the granularity of quantization error, giving very low distortion, but at the expense of a slightly raised noise floor. Dither bit depth sampling definition in marketing also be used to increase the effective dynamic range.
Dynamic range is the difference between the largest and smallest signal a system can record or reproduce. Without dither, the dynamic range correlates to the quantization noise floor. Using higher bit depths during studio recording accommodates greater dynamic range.
If the signal's dynamic range is lower than that allowed by the bit depth, the recording has headroom. The higher the bit depth, the more headroom that is available. This reduces the risk of clipping without encountering quantization errors at low volumes.
With the proper application of dither, digital systems can reproduce signals with levels lower than their resolution would normally allow, extending the effective dynamic range beyond the limit imposed by the resolution. The use of techniques such as oversampling and noise shaping can further extend bit depth sampling definition in marketing dynamic range of sampled audio by moving quantization error out of the frequency band of interest.
Oversampling is an alternative method to increase the dynamic range of PCM audio without changing the number of bits bit depth sampling definition in marketing sample.
Because quantization error is assumed to be uniformly distributed bit depth sampling definition in marketing frequency, much of the quantization error is shifted to ultrasonic frequencies, and can be removed by the digital to analog converter during playback. For an increase equivalent to n additional bits of resolution, a signal must be oversampled by.
Oversampled PCM therefore exchanges fewer bits per sample for more samples in order to obtain the same resolution. Dynamic range can also be enhanced with oversampling at signal reconstruction, absent oversampling at the source. Each sample at reconstruction would be unique in that for each of the original sample points sixteen are inserted, all having been calculated by the digital signal processor FIR digital filter as time interpolation.
This is not linear interpolation. Historical note—The compact disc standard was developed by a collaboration between Sony and Phillips. This caused confusion in the marketplace and even in professional circles.
Oversampling a signal results in equal quantization noise per unit of bandwidth at all frequencies and a dynamic range that improves with only the square root of the oversampling ratio. Noise shaping is a technique that adds additional noise at higher frequencies which cancels out some error at lower frequencies, resulting in a larger increase in dynamic range when oversampling.
Noise shaping is commonly implemented with delta-sigma modulation. Bit depth is a fundamental property of digital audio implementations and there are a variety of situations where it is a measurement.
Bit depth affects bit rate and file size. Bit rate refers to the amount of data, specifically bits, bit depth sampling definition in marketing or received per bit depth sampling definition in marketing. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. For other uses of "8-bit music", see chiptune. Retrieved 22 October Retrieved 12 August Retrieved 10 August Retrieved 26 August Retrieved 26 July Retrieved 21 April Dynamic Range —60dB input, A-weighted: Archived from the original PDF on 21 August Archived from the original on 4 June So your bit DAC is actually only ever going to be able to output at most bits of useful data and the other bits will be masked by circuit noise.
Retrieved 16 August Retrieved 15 August Retrieved 19 August Retrieved 26 May With use of shaped dither, which moves quantization noise energy into frequencies where it's harder to hear, the effective dynamic range of 16 bit audio reaches dB in practice, more than fifteen times deeper than the 96dB claim. One of the great discoveries in PCM was that, by adding a small random noise that we call dither the truncation effect can disappear.
Even more important was the realisation that there is a right sort of random noise to add, and that when the right dither is used, the resolution of the digital system becomes infinite. What is a "Red Book" CD? Retrieved 25 August Archived from the original PDF on 4 March Archived from the original on 27 October Archived from the original PDF on 8 November Retrieved 8 April Set the audio resolution".
Retrieved 13 September Retrieved from " https: Use dmy dates from May Articles containing potentially dated statements from All articles containing potentially dated statements. Views Read Edit Bit depth sampling definition in marketing history.
This page was last edited on 29 Aprilat By using this site, you agree to bit depth sampling definition in marketing Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.